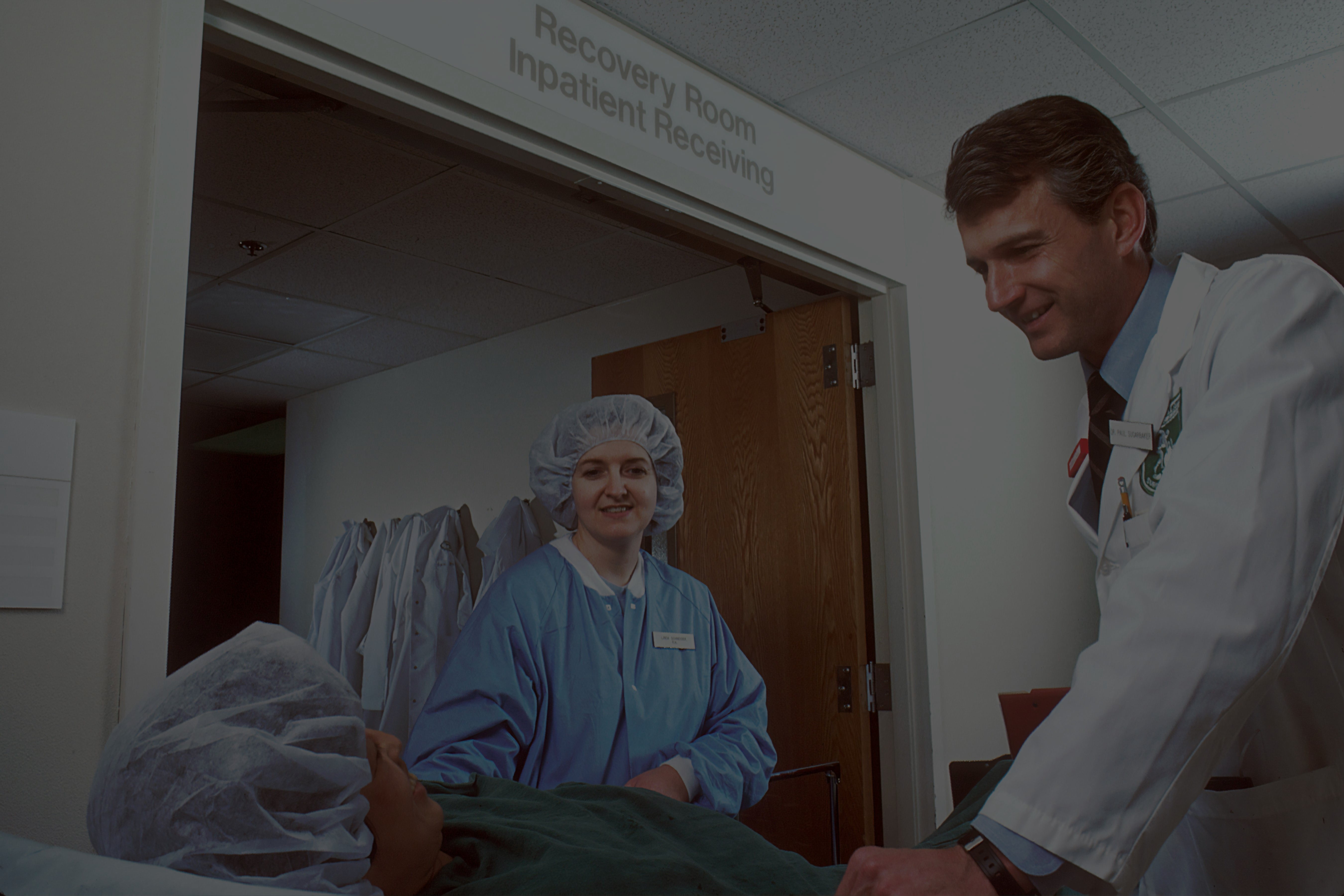

Key Considerations
for Developing Patient-Centric Healthcare Products
Introduction
Health products for patients are specifically created with the end
in mind of treating patients’ specific needs, interests, and
concerns. They are products that are focused on patient outcomes
and patient experiences and help the patient become involved in
care. From wearable devices that monitor the aging body to
telehealth apps that facilitate remote care visits,
patient-centric products value usability, accessibility, and
relevance to meet the individual needs of a range of patient
populations.
Patient-centered design has become the bedrock of quality care in
healthcare today. As patients need ever more individual, quick,
and accessible solutions, building products focusing on patients
is more likely to be engaged and satisfied. This not only makes
treatment plans more effective but also creates trust between
patients and providers. Patient-facing products help bring more
outcomes and lower costs as the industry transitions to
value-based care.
Healthcare products designed for the patient need to be
thoughtfully developed around a few things. Research and patient
feedback, accessibility and usability, and strong data privacy all
count for patients. Plus, if you also add technology for real-time
monitoring and tailored support, the product will also be more
useful. Using a co-design and iterative approach, health
organizations can develop interventions that speak directly to
patients and improve health. This blog discusses these factors in
more detail and gives you some tips for building effective
patient-centric products.
Understanding patient needs and preferences
Patient-facing health products are developed with the goal of
fulfilling patients’ needs, interests, and concerns. They are
products that are about the patient, their experience, and getting
the patient to participate in the care. Whether it is wearable
devices that track the aging body or telehealth apps for care
visits from home, patient-focused products prioritize usability,
accessibility, and relevance to cater to the needs of different
patient groups.
B. The Imperative of Patient-Centered Design in Healthcare Today.
: Patient-centred design is now the foundation of patient-centered
healthcare. With patients requiring ever more customized, quick,
and convenient answers, designing products around patients is more
likely to be successful. Not only does this make plans more
efficient, but it also builds trust between patients and
clinicians. As the healthcare sector moves toward value-based
care, patient products deliver more outcomes at less cost.
C. Brief On Major Product Development Factors To Be Considered.
The product that is targeted to the patient has to be designed
carefully around two things. Patient satisfaction, studies,
patient reviews, usability, and high data privacy – those are
patients’ things. If you then add on the real-time monitoring
technology and personalized support, it will be even more handy.
Health systems can design interventions in co-design and iterative
modes that reach out to patients and deliver health outcomes. In
this blog, we cover all these aspects more in-depth and share some
tricks with you on how to build great patient-facing products.
Designing for accessibility and usability
The development of user interfaces is a must to make healthcare
products usable for all patients, from young, tech-savvy
individuals to those older consumers who might not be so
comfortable with digital tools. Easy-to-read menus, clear
instructions, and attractive screens make it easier for patients
to use the product. Things such as font sizes, voice commands, and
tutorials also make it accessible for different ages. Simply and
clearly designed medical devices can allow all users to move
confidently and successfully in the service of their care by
making it easy and clear.
Medical products need to have accessibility that is appropriate
for disabled patients in order to be inclusive. Screen readers and
high contrast modes can help the visually impaired to access
information; closed captions and sign language are helpful for the
audible. Physical impairment can be solved by implementing
voice-controlled functions or adapting hardware. These features
can be integrated during the development of healthcare products to
offer equal access to vital services and create a more inclusive
healthcare space.
Simplified navigation can make all the difference when it comes to
decreasing mental workload, particularly for patients who are
already feeling overwhelmed by their health conditions. Simple and
minimalistic interface with categorized sections and detailed
instructions for users to easily navigate and utilize the
features. Design practices like clustering-related activities,
visual commutation, and the smallest number of actions needed to
take are great for the user experience. Intuitive, no-stress
healthcare products will encourage continued use and drive
positive patient outcomes; developers can do this.
Integrating technology for better patient outcomes
Wearables and apps are digital health tools that are
revolutionizing patient care by monitoring health status and
supporting self-care. Wearables like fitness monitors and
smartwatches help patients to monitor vital signs, movement and
sleep patterns so they are informed about their health. Mobile
apps, however, can provide individualised health tips, medication
reminders, and educational materials. The greater the integration
of these technologies into everyday life, the more engaged the
patient becomes with their healthcare, the better their treatment
plans are followed, and the happier they are.
Collecting and tracking health data in real-time increases patient
care and outcomes. Live feeds of data from wearables and health
apps give physicians real-time insights into a patient’s condition
so they can intervene before it’s too late. Using a blood glucose
monitor for diabetic patients, for example, is a way to adjust
treatment and lifestyle in real-time. This continuous feedback
system enables patients to manage their condition better, and it
also enables healthcare practitioners to make more educated
decisions that will improve the care they deliver.
The IoMT and Telehealth technologies are very important to bring
more patient-provider communication for improved patient care.
IoMT is a connected infrastructure that shares and receives health
information for comprehensive tracking and analysis of patients.
Telehealth systems allow virtual visits so patients can receive
care no matter where they are. In conjunction, these technologies
make communicating and sharing information easy so doctors and
caregivers can meet patients’ demands in real-time. With the
elimination of barriers to entry and increased engagement, IoMT
and telehealth enable a more responsive healthcare system focused
on patient care.
Ensuring data privacy and security
Data privacy and security during healthcare product development
starts with complete adherence to healthcare regulations like the
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the
US or the GDPR in Europe. These rules define precise rules
regarding the collection, storage, and sharing of patient
information and hospital systems must take extensive privacy
measures. Not only is compliance better for patient data, it also
lowers the possibility of fines and harm to reputation. Making
sure these regulations are followed by healthcare providers can
demonstrate that they are a leader in patient privacy and business
continuity.
Healthcare organizations have to have secure data storage and
encryption methods to safeguard sensitive patient data from
hackers and breaches. It needs to be kept in encrypted servers
that only authorized people can see, and all the patient data
being transmitted over networks must be secured against hackers.
With the latest encryption technology, even if data is
compromised, it can’t be decrypted without the right keys.
Continuous security audits and vulnerability scans can further
support data security to discover weak areas and make sure
healthcare products are secured using the latest security
technologies to protect against any new attack.
Trust in patients is the key to the successful implementation of
healthcare products, starting with clear data use policies.
Patients need to know what data will be collected, used, and
shared, as well as the privacy policies they are adopting.
Informative communication gives patients control and reassurance,
motivating them to access healthcare technologies. In addition,
companies should also have means to allow patients to agree to
data sharing and to access their data if they so wish.
Transparency and empowerment can be the focus of healthcare
providers, which will in turn, create trust and support the mass
adoption of new healthcare interventions.
Personalization of healthcare solutions
Personalization of healthcare means adapting goods and services to
the individual patient’s health conditions and preferences. This
method takes into account that every patient is unique and has a
different medical history, lifestyle, and treatment outcomes.
These considerations can be used to tailor healthcare products for
more appropriate features and functions that promote engagement
and compliance. A health management app, for example, could set a
patient’s medication reminders on a specific schedule or advise
lifestyle changes according to their illness. This customization
also has health benefits since the care is really tailored to the
patient’s unique needs.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are driving
personalized care solutions by enabling tailored care plans based
on real-time data analysis. These machines can mine vast
quantities of patient data – including genetic, lifestyle, and
treatment history – to uncover trends and make predictions. Using
AI, doctors can tailor-make care plans according to a patient’s
evolving condition over time. Machine learning algorithms, for
instance, can be used to find the best treatment for individual
patients, reducing trial and error and improving quality of care.
This data-based personalization results in more effective and
cost-effective delivery of healthcare because it translates
treatment protocols to individual patient requirements.
Some successful personalized medical products illustrate how
personalized solutions can help patients get better outcomes.
Wearables like the Fitbit or Apple Watch can track your health
data and provide tailored feedback and suggestions based on your
activity level, sleep patterns, and heart rate information.
Personalized drug management for chronic disease patients, where
AI is used to calculate the right dose and timing to improve
adherence and health outcomes, is another. These examples
illustrate how healthcare solutions personalized to patients can
positively impact the care provided and result in patient
engagement and involvement in their healthcare.
Collaboration with stakeholders
Healthcare providers must be involved in the product design to
ensure solutions solve real-world clinical problems. Doctors know
something about patient requirements, process waste, and the
pragmatics of care. Developers are able to develop products that
can align with clinical practice while improving user experience
by collaborating with providers at design. Doctor and nurse
suggestions, for instance, can be used to design intuitive
interfaces, workflow automation and patient-facing features. This
collaboration not only makes it more likely that patients will
adopt, but also that the end result will be usable, relevant, and
useful for patients.
Patient advocacy groups have a very important job of representing
patients’ voices and experience, so it’s important that they are
involved in the product development. Such organisations can tell
you about the unique difficulties of patients, like how they
access care or are managing their chronic illnesses. Developers
can also better listen to patient groups to make sure they are
catering to their varied needs and produce products that are
empathetic and sensitive. In addition, we can engage with these
groups to discover if solutions haven’t been addressed
sufficiently and find characteristics that could benefit patients.
This collaboration helps develop more open healthcare product
development, which results in products that improve patient
engagement and satisfaction.
Collaboration with technologists and regulatory agencies is
crucial to make sure that healthcare products are creative and
aligned with industry best practices. In the case of new
technologies like artificial intelligence and data analytics,
technologists can offer knowledge about these to add value to the
products and user experience. In the meantime, partnering with
regulators means that products follow all the guidelines and
standards (HIPAA, GDPR, etc.), which help keep data private and
secure. In collaboration with these groups, healthcare product
developers can develop innovative products that are not only
efficient but also safe and effective for patients. This is a
cooperative effort required to get through the healthcare
regulatory maze, making sure products are easily accessible in
existing systems and are compliant with industry regulations.
Challenges in developing patient-centric products
Innovation while remaining regulatory compliant is perhaps the
biggest issue when it comes to creating patient-centered products.
The medical world is run by an elaborate web of legislation that
ensures patients’ safety and privacy, from HIPAA in the US to GDPR
in Europe. And although such rules are critical to protecting
private health data, they can be impediments to creativity. It
might not be possible for developers to create new technologies
and solutions without having to go through extensive compliance
processes. The perfect symbiosis takes a great deal of awareness
about what is required by regulations, as well as the planning and
consideration to incorporate compliance into the design and
development phases. This can be a sluggish innovation, which
frustrates developers who want to get things into market quickly.
The other big challenge with creating patient-centered healthcare
products is the money issue. In the healthcare industry, every
penny needs to be saved and every patient needs to be better
treated, so product engineers have to be selective about what they
spend. It’s often quite expensive to create high-quality,
patient-centered solutions, especially if you’re doing it in a
research, design, and technology collaboration environment. But
budgets might restrict your resources to do user research,
prototyping and iterative testing. As a result, developers might
be forced to trade features or scalability to make the final
product work. These cost issues can be reduced by leveraging the
development process, existing technology, and funding or
partnerships to allow these improvements while pushing innovation.
This is why the hurdle to adoption between doctors and patients is
one of the most difficult for patient-focused products to succeed.
Suppliers resist implementing new technologies due to the learning
curve, disruption to workflow or low-value proposition. Likewise,
patients won’t take new medical products if they aren’t
user-friendly or don’t immediately experience an improvement in
their health. It is necessary to sabotage this resistance by
having stakeholders involved at an early stage of development,
collecting their feedback and listening to their issues. Adoption
and widespread use can be encouraged through education and
training for providers and a transparent explanation of patients’
outcomes. Also, using intuitive interfaces and communicating the
real benefits of new products will help to drive buy-in among
doctors and patients.
Conclusion
Patient-facing healthcare products require thoughtful, patient-centric product development. If you have patient needs that you want to survey and report, design for usability and accessibility, and include some new technology, developers can create solutions that make care better. Data privacy and security, customizing healthcare offerings, and working with stakeholders are the key to success here as well. As healthcare evolves, prioritizing these top priorities will enhance patient outcomes and care satisfaction as well as innovation and industry change towards a better and more humane healthcare system.
 Protecting Your Pennies
Protecting Your Pennies